voluba
A browser-based tool for interactive alignment of volumes of interest to 3D reference templates.
- Spatially align your volume of interest to rodent and human reference templates in a web browser.
- Adjust position, scale, orientation and anatomical 3D landmark pairs interactively while appreciating the full resolution of the data.
- See the aligned volume in combination with brain maps in the atlas viewer siibra-explorer.
- Store or share the parameters and resulting transformations.
Using voluba, you can upload an image file to a private storage space and register it interactively to a reference space in your web browser. Currently, voluba supports the BigBrain model, Waxholm rat template and Allen mouse template as reference spaces. voluba is compatible with siibra-explorer, so you can directly inspect your aligned data superimposed with brain region maps and other datasets. You can also submit your anchoring result to EBRAINS curation support for sharing.
Anchoring high-resolution partial volumes to a reference model
Working on a proper anchoring of high-resolution imaging data to a reference template is out of reach for many neuroscientists due to the sheer size of the datasets and the lack of available tools. Here, we present the interactive alignment tool voluba, which allows anchoring of volumetric image data to reference volumes at microscopical spatial resolutions. It is implemented as a web service and offers a highly interactive workflow.
Select reference space and input volume
Log in with your ORCID or EBRAINS account to upload a dataset into your private working space for the anchoring process. You can choose between rat, mouse and human reference volumes.
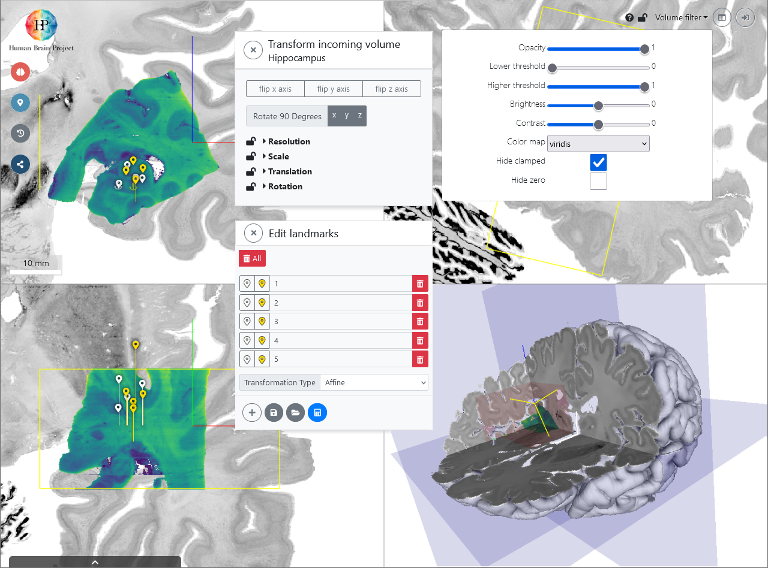
Adjust appearance of the input image
The input volume is presented as a graphical overlay in a 3D view with orthogonal cross sections. To optimize the visualization you can customize contrast, brightness, colormaps, and intensity thresholds.
Interactive alignment
You can directly manipulate the relative position and orientation of the input volume with your mouse point, and adjust voxel scaling and axis orientations in a separate window. These settings determine a rigid transformation.
Refine with 3D anatomical landmarks
You can use voluba's 3D landmark editor to refine the transformation by specifying pairs of corresponding anatomical points between the volumes. This step is further facilitated by an optional side-by-side view. From a set of landmarks, the transformation is recalculated with additional degrees of freedom, including shearing.
Use the anchoring result
You can download the resulting transformation parameters in JSON format, which can be re-imported in voluba, and due to its simple structure be utilized in other tools and workflows. Alternatively, you can export your uploaded image data to NIfTI format with an updated affine. To share your anchored image, you can also obtain a private URL. If you would like to publish the transformation parameters of the anchored result to EBRAINS, voluba offers an automatic workflow for submission to the EBRAINS Knowledge Graph. Most importantly, the aligned image can be opened in the atlas viewer siibra-explorer to see it in the anatomical context of the Human Brain Atlas.
Other Tools
See all toolsCreate an account
EBRAINS is open and free. Sign up now for complete access to our tools and services.