QUINT workflow
Extract, quantify and analyse features from rodent histological images
The QUINT workflow takes you through steps to quantify and analyse labelled features within a known atlas space.
- Leverage a streamlined, tested workflow for analysing labelled features in large numbers of histological sections from mouse or rat
- Obtain quantitative measures in atlas-defined regions
- Customise the granularity of regions-of-interest to fit the needs of your analysis
The QUINT workflow comprises a suite of software designed to support atlas-based quantification. All the software have user interfaces, with no coding ability required. It generates object counts and percentage coverage per atlas-region, in addition to point clouds for visualising the features in 3D.
It currently supports quantification relative to the following atlases:
- Allen Mouse Brain Atlas Common Coordinate Framework version 3 (2015 and 2017) (CCFv3)
- Waxholm Atlas of the Sprague Dawley rat, version 2, 3 and 4 (WHS rat brain atlas).
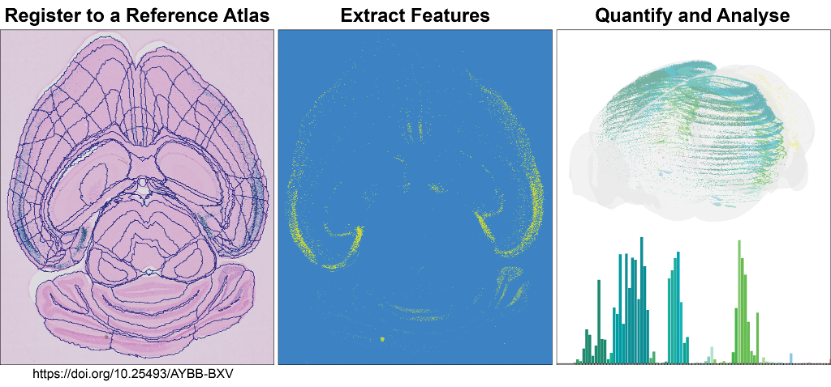
Analyse large amounts of histological image data from rat or mouse brains
Nutil
ilastik
QuickNII
VisuAlign
MeshView
QCAlign
Use QUINT for:
- Cell count analysis
- Analysis of tract-tracing connections
- Resizing, rotating and renaming large Tiff images
Access a QUINT dataset on EBRAINS
Use Nutil to edit large Tiff images
Get involved in the QUINT community
Are you interested in atlas based spatial quantification? Discover the QUINT workflow and interact with us to customise the workflow for your needs: Count cells, AD plaques and quantify connectivity traces in 2D images from mice and rat. The QUINT workflow is highly flexible and has developed over time in response to users’ needs. We look forward to continuing this collaboration with the research community and welcome all requests, big and small. Post us questions directly through github or at https://ebrains.eu/support/
Github Nutil/ QUINT
Github QuickNII/VisuAlign
Github ilastik
Course Neuroscience data integration
Related Publications
See all publicationsRelated Resources
See all resourcesQUINT user manual
Other Tools
See all toolsCreate an account
EBRAINS is open and free. Sign up now for complete access to our tools and services.